The Characteristics of a Physical Change, how it occur in scientific procedure

The Characteristics of a Physical Change, how it occur in scientific procedure
The following are the characteristics of a change that can reformed again, which no new one renewed known as physical change
Describe the characteristics of a physical change
Physical change
Substances may undergo changes in their physical properties e.g. changes in colour, shape (or form), state, density, structure and texture, etc. If you take a stone and break it down into small particles, you will have only changed its form, but it will remain as a stone. Likewise, melting ice to water or freezing water to ice does not change it, but it is still water. The same case happens when you dissolve salt in water to get a solution of salt in water. You can still get back the original salt by evaporation, except that the crystals of the salt obtained will not look exactly the same as those of the original salt.
These changes of state are examples of physical changes. Physical changes such as melting and boiling do not result in new substances being formed
For example, ice and water still contain the same particles whether in solid (ice) liquid (water) or gaseous (vapour) state.
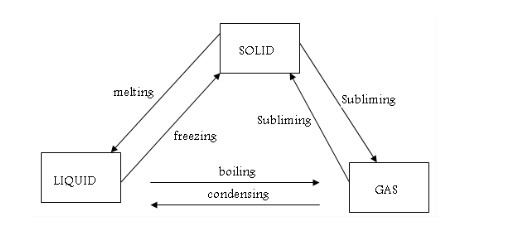
Changes in states
Characteristics
In the explanation above, we find that in a physical change it is only the physical form, and not the actual nature, of a substance that changes. The changes are brought about by a mere addition or removal of heat, as in the case with water or ice. Such a change is called a physical change. It can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- There is no formation of a new substance. Consider an example given above. The ice, liquid water and steam are the solid, liquid and gaseous forms of the same substance (water).
- There is no change in weight of the substance undergoing the change. If you start with 50g of ice, you will still get the same mass of water and steam (vapour) upon melting and boiling respectively.
- The changes are readily reversible. You can easily change water back to ice and vapour to water by a mere subtraction of heat (cooling).
- It is not accompanied by a great heat change. Just a little heat is required to change ice to water, and water to steam.
Physical Changes of Matter Experimentally
Demonstrate physical changes of matter experimentally
Experiment
- Add some common salt (sodium chloride) to distilled water in a beaker. Stir the mixture until the salt disappears and forms a solution with water. Transfer the water into a porcelain dish. Heat the content until all the water has evaporated off. The salt reappears in its original white solid form.
- Grind some roll sulphur in a mortar to powder. Put the resultant powder in a test-tube and heat gently, shaking all the time. The sulphur melts to an amber-coloured liquid. On cooling, this liquid returns to its original condition as a yellow solid.
- Put a block of ice in a beaker. Heat gently until the whole block melts to form water. Pour the water formed in a cup and place it in a deep freezer overnight. The water will freeze back to ice.
You will have seen that all the above changes involve only changes in physical forms of the substances. The chemical nature of substances remained unchanged. Therefore, we can define a physical change as a change that does not involve formation of a new substance but involves a change in state or physical form of the substance and that such a form can be reversed.
The Characteristics of a Chemical Change
Describe the characteristics of a chemical change
Chemical change
Some changes that materials undergo are permanent. Such changes usually involve changes in chemical properties of a substance. For example, when you burn a piece of wood in fire, you get ash. The properties of wood and ash are very different. There is no way you can change ash back to wood. It is practically impossible. A permanent change in chemical properties of a substance is called a chemical change. In a chemical change, a substance losses all its physical and chemical properties.
Characteristics
Includes
- A chemical change results in the formation of a new substance. The new substance has different chemical and physical properties as compared to the original substance.
- It is generally not reversible. For example, you cannot turn the ash back to wood.
- There is a change in weight or mass of the substance undergoing the change. When you burn wood weighing 5 kg, you cannot expect to get the same weight of ash.
- The change is accompanied by a considerable heat change. For wood to burn to ash a lot of heat must be supplied.
Chemical Changes of Matter Experimentally
Demonstrate chemical changes of matter experimentally
Experiment
- Strongly heat some roll sulphur on a deflagrating spoon until it melts and begins to burn with a blue flame. If you continue heating, it gradually decreases in amount and finally the spoon will be left empty. The disappearance of sulphur is due to the formation of a new gaseous substance that is invisible. The presence and existence of a gas in air can be defected by its irritating smell. The gas can also be detected by burning the sulphur in a gas jar to which some blue litmus solution has been added. The gas formed, sulphur dioxide, will turn the blue litmus paper into a red one.
- With the aid of tongs, subject a piece of magnesium ribbon to a Bunsen burner flame. The ribbon burns to produce a new substance, white ash of magnesium oxide.
- Wrap a wet cotton wool around an iron nail. Keep it in a test tube for 3 days. By the 3rd day, some brown marks of rust will appear on the surface of the nail. Rust is hydrated iron (III) oxide. This is quite a new substance compared to iron nails.
Table
Differences between physical and chemical changes
| Physical change | Chemical change |
| 1. Produces no new kind of matter | Always produces a new kind of matter |
| 2. There is no change is mass or weight of the substance | 2. There is a substantial change in the weight of the substance |
| 3. The change can be reversed | 3. The change cannot be reversed |
| 4. Little heat is absorbed or evolved | 4. Heat changes may be large |
|
5. The change involves only a change in physical properties of a substance
Generally physical change is just change that can be reformed again no any effect so it need little heat though no mass or weight doesn't change |
Tags
Comment / Reply From
You May Also Like
Popular Posts
Newsletter
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!
Categories
- Places and Regions (349)
- Health & Science (3559)
- Jobs (188)
- Work Life (286)
- Opinions (426)
- Real estate & Properties (121)
- Shipping & Logistics (64)
- Sex & Relationships (1755)
- Movies & Animation (6102)
- Comedy (229)
- Travel and Events (427)
- Gaming (1185)
- History and Facts (1296)
- People and Nations (1020)
- Science and Technology (3704)
- Arts & Entertainment (1810)
- Life Style (3627)
- Education (3386)
- Economics and Trade (1950)
- Others (5396)
- News and Politics (3218)
- Cars and Vehicles (430)
- Pets and Animals (326)
- Digital Marketing & Web Develpment (4)
- Robotics, VR & AR (0)
- DFTUntoldStories (1)
- Celebrities (83)
- Mobile Solutions & Apps (0)
- Ecommerce & Clean Tech (0)
- Artificial Inteligence & IoT (0)
- Big Data & Cyber Security (0)
- Business (1780)
- Palscity Show (0)
- Sports Show (0)
- Politics & Leadership Show (0)
- Digitally Fit Show (0)
- Entertainment & Lifestyle Show (0)
- Business Show (1)
- In The Morning Show (0)
- DFT Reels & Shorts (0)
- Natural & Food (1141)
- People and Culture (11)
- Sports (1906)
- Fashion (116)
- Gossip (55)
- Music (116)